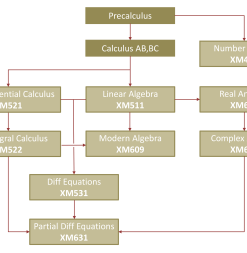
Prerequisites
The flowchart below outlines what course(s) students should begin with. In order to enroll in a course, students must satisfy the given prerequisites or the equivalent.
Courses
Multivariable Differential Calculus (XM521)
Differential calculus for functions of two or more variables. Topics: vectors and vector-valued functions in 2-space and 3-space, tangent and normal vectors, curvature, functions of two or more variables, partial derivatives and differentiability, directional derivatives and gradients, maxima and minima, optimization using Lagrange multipliers.
Prerequisites: Calculus AB, BC (or Calc I, II) or equivalent.
Required text: Calculus: A New Horizon, 6th edition (or later).
Multivariable Integral Calculus (XM522)
Integral calculus for functions of two or more variables. Topics: double and triple integrals, change of variables and the Jacobian, vector fields, line integrals, independence of path and the fundamental theorem of line integrals, Green's theorem, divergence theorem, and Stokes' theorem.
Prerequisites: Multivariable Differential Calculus or equivalent.
Required text: Calculus: A New Horizon, 6th edition (or later).
Linear Algebra (XM511)
An introductory course in Linear Algebra. Topics: matrices, linear equations, vector spaces, bases, coordinates, linear transformations, eigenvectors, eigenvalues, and diagonalization.
Prerequisites: Calculus AB, BC or equivalent.
Required text: Linear Algebra, Bronson.
Modern Algebra (XM609)
Theory of abstract algebra, with particular emphasis on applications involving symmetry. Topics: groups, quotient groups, symmetry groups in three dimensions, Pólya-Burnside method, rings and fields, polynomial and Euclidean rings, quotient rings, field extensions, and geometrical constructions.
Prerequisites: Multivariable Calculus, Linear Algebra or equivalent.
Required text: Modern Algebra and Applications, Gilbert.
Real Analysis (XM615)
Theory of functions of a real variable. Topics: sequences, series, limits, continuity, uniform continuity, sequences and series of functions, uniform convergence, differentiation.
Prerequisites: Calculus, Linear Algebra or equivalent. [Proof-writing experience is desirable.]
Required text: Elementary Analysis: The Theory of Calculus, K. Ross.
Complex Analysis (XM606)
Theory of differentiation and integration of complex functions. Topics: algebra of complex numbers, complex functions, multi-valued functions, exponentials, logarithms, analyticity, integrals, power series, Laurent series, residues, isolated singularities, poles and zeros.
Prerequisites: Calculus, Real Analysis, Linear Algebra or equivalent.
Required text: Complex Variables and Applications, Brown and Churchill.
Differential Equations (XM531)
Basic techniques and methods for solving ordinary differential equations. Topics: linear, separable, and exact equations, existence and uniqueness theorems, difference equations, basic theory of higher order equations, variation of parameters, undetermined coefficients, series solutions, Laplace transform, systems of equations.
Prerequisites: Multivariable Differential Calculus, Linear Algebra or equivalent.
Required text: Elementary Differential Equations, Boyce and DiPrima, 6th edition (or later).
Partial Differential Equations (XM631)
Theory of differential equations involving functions of more than one variable. Topics: first order equations, classification of second order equations, initial-boundary value problems for heat equation, wave and related equations, separation of variables, eigenvalue problems, Fourier series, existence and uniqueness questions.
Prerequisites: Multivariable Calculus, Linear Algebra, Differential Equations, Real Analysis, Complex Analysis or equivalent.
Required text: Partial Differential Equations, An Introduction, W. Strauss.
Number Theory (XM452)
Introduction to number theory and its applications. Topics: Euclid's algorithm, divisibility, prime numbers, congruence of numbers, theorems of Fermat, Euler, Wilson, Lagrange's theorem; residues of power, quadratic residues; magic squares; continued fractions; Diophantine equations; quadratic fields and quadratic integers.
Prerequisites: Precalculus or equivalent. [Proof-writing experience, participation in math competitions are desirable.]
Required text: An Introduction to Number Theory, Stark.